Chlamydia Pneumoniae diagnostic
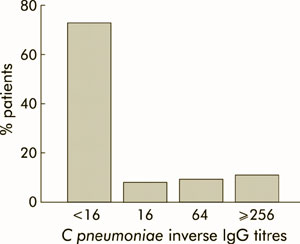
The diagnosis of Chlamydia pneumoniae infection in patients with rheumatoid arthritis is often contradictory. In this study, 106 patients were examined with rheumatoid arthritis without symptoms of Chlamydia pneumoniae infection. In the patients IgG, IgA and IgM antibodies against Chlamydia pneumoniae were measured by ELISA. The IgA antibodies were measured a second time from the same sample after absorption of IgG and rheumatoid factor. 8.4% of patients had IgM antibodies, in contrast to only 1% in the general population. Because of these frequent false positive results and the fact that IgM antibodies during acute infection also often missing, the determination of IgM antibodies for the diagnosis of Chlamydia pneumoniae infection in patients with chronic polyarthritis is only of limited use. 48.5% of patients had IgA antibodies. After absorption, the IgG-IgA antibodies in 67% of patients were positive. This high level of seropositivity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis shows that in the clinic often guided by the determination of a single IgA value can rarely be useful, it should be a pair of samples are sent at intervals of several weeks to an increase in titer festzusellen.
The determination should be performed only when a clear clinical suspicion of Chlamydia pneumoniae infection and are not "made ??it to safety," since in these cases a positive result is hardly recover. It should also be conducted in the future prior to the determination of IgA antibodies are IgG absorption, otherwise false negative results or expected to have low titers. 55% of patients had IgG antibodies. This shows that Chlamydia pneumoniae infections do not occur in patients with chronic polyarthritis despite their immunosuppressive medication frequently.
|
|
© 2014 "chlamydia-pneumoniae.org". All Rights Reserved |